NOZZLE SELECTION GUIDELINES
Why Nozzle Selection is Important
Criteria for Selecting a Nozzle
Spray Patterns
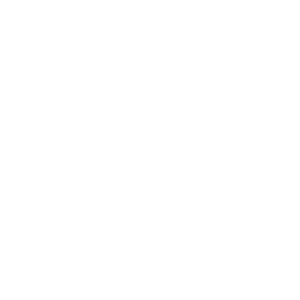
Droplet Size
Droplet size is often critical. Many processes such as gas scrubbing depend on exposing the maximum possible liquid surface to a gas stream. Other applications require that the droplets be as large as possible, such as when the spray must project into a fast-moving gas stream. Exposing the maximum surface area requires breaking the liquid into droplets as small as possible.
To get an idea of how this works, imagine a cube of water with a volume of 1 gallon. This cube has a surface area of 1.6 ft2. If we split it in two, we expose some inner surfaces and increase the total surface area to 2.1 ft2.
Atomizing the liquid into spheres 1 mm (1,000 microns) in diameter would increase the surface area of this gallon of liquid to 244 ft2. A nozzle produces a range of droplet sizes from the solid-liquid stream. Since it is inconvenient to list all the sizes produced, droplet size (in microns) is usually expressed by a mean or median diameter.
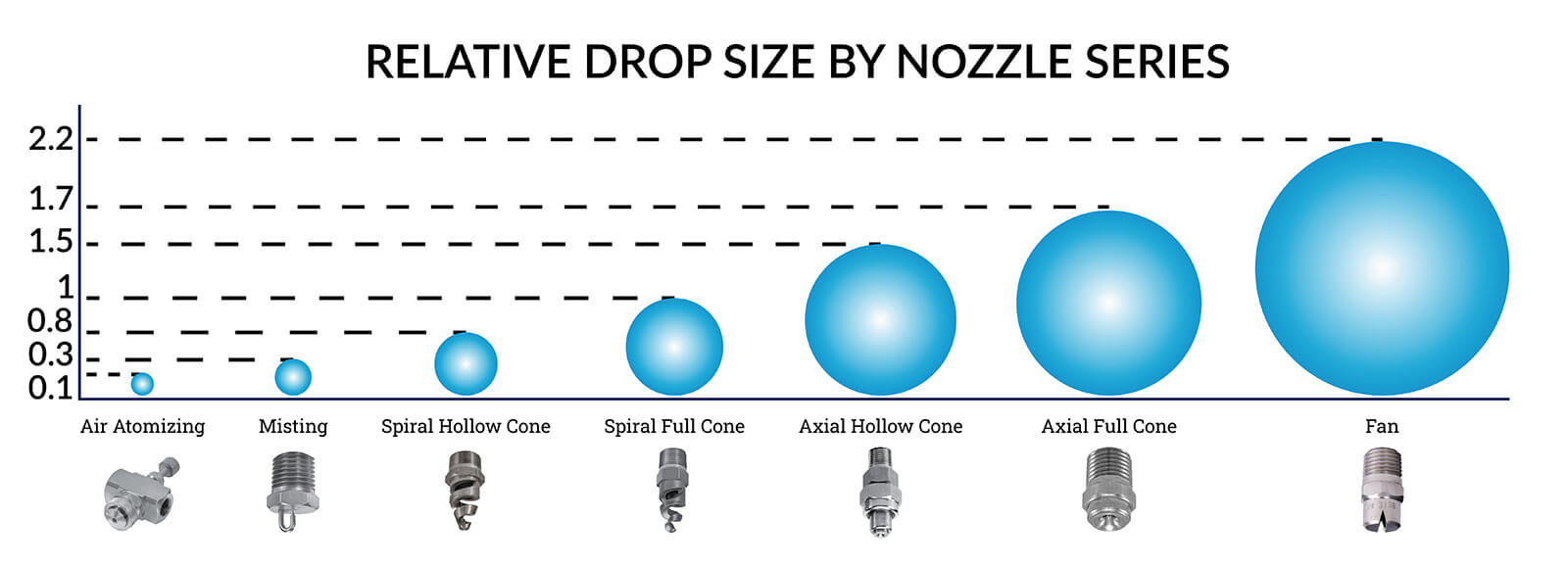
Spray Coverage
Four terms are commonly used to describe spray coverage.
Spray Angle(A) The included angle of the spray is measured close to the nozzle orifice. Since the droplets are immediately acted upon by external forces (gravity and moving gases, for example), this measurement is useful only for determining spray coverage close to the nozzle. The spray angles listed for nozzles in this catalog are angles at the nozzle, measured at the nozzle's design pressure, highlighted in each chart of flow rate vs. pressure.
Actual Spray Coverage(B) The actual coverage at a specified distance (D) from the nozzle.
Effective Spray Angle(C) The angle calculated from the actual coverage (B) at a distance (D).
Theoretical Spray Coverage(E) The coverage at a distance (D) if the spray moved in a straight line.
Flow Rate
ΔP = Supply pressure at nozzle inlet / external pressure at the nozzle outlet
Higher ΔP = higher flow rate
Lower ΔP = lower flow rate
Material Considerations
Some factors that influence the nozzle material selection process are: